Pound Sterling gains as investors shrug off increased BoE dovish bets

- The Pound Sterling rises against its major peers as investors look beyond the mild increase in BoE dovish bets for 2025.
- The revised UK GDP estimates for Q3 show that the economy remained flat.
- The latest commentary by Fed officials shows less willingness to cut interest rates in 2025 amid uncertainty surrounding Trump’s policies.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) moves higher against its major peers on Monday as investors largely ignore a mild increase in Bank of England’s (BoE) dovish bets for the next year. Traders see a 53-basis points (bps) reduction in interest rates in 2025, up from 46 bps after the BoE policy announcement on Thursday.
BoE dovish bets accelerated after three out of nine Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) members proposed reducing interest rates by 25 bps, more than the one projected by market participants. Investors considered the 6-3 vote split as a dovish buildup for the next year, which weighed heavily on the Pound Sterling.
Market expectations for 53 bps reduction in interest rates in 2025 suggest that there will be at least two 25-basis-points rate cuts. Still, speculation for the number of interest rate cuts by the UK central bank is similar to that of the Federal Reserve (Fed) and fewer than those expected from the European Central Bank (ECB), making the Pound Sterling an attractive bet in the broader term.
On the contrary, analysts at Deutsche Bank expect the BoE to announce four interest-rate cuts next year, one coming in the first half and the rest in the second half.
Meanwhile, data released on Monday downwardly revised the UK growth rate for the third quarter of the year, raising concerns over the United Kingdom’s (UK) economic outlook. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) reported that the economy remained stagnant in the third quarter, against the 0.4% growth in the April-June period and less than the 0.1% expansion previously estimated.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling trades higher
- The Pound Sterling consolidates around 1.2580 against the US Dollar (USD) in Monday’s London session. The GBP/USD pair ticks slightly up even as the US Dollar rebounds slightly. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which gauges the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, recovers to near 108.00.
- The Greenback discovers buyer’s interest as its broader outlook is upbeat amid firm expectations that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will follow a moderate policy-easing approach next year. In the latest dot plot, the Fed signaled only two interest rate cuts in 2025 against the four cuts projected in September. For January’s policy meeting, traders are pricing in that the central bank will leave interest rates unchanged in the range of 4.25%-4.50%, according to the CME FedWatch tool.
- The latest commentaries by Fed officials have shown that stubborn inflation, better labor market conditions than previously anticipated, and uncertainty over the impact of President-elect Donald Trump's incoming policies on the economy forced them to guide fewer interest rate cuts for 2025.
- Cleveland Fed President Beth Hammack, the only official who dissented against the rate-cut decision in the policy meeting on Wednesday, said on Friday: “I prefer to hold policy steady until we see further evidence that inflation is resuming its path to our 2% objective.”
- This week, thin trading volume due to holidays in Forex markets on Wednesday and Thursday on account of Christmas Day and Boxing Day, respectively, could keep the pair’s price action more muted.
- On the economic front, investors will focus on the United States (US) Durable Goods Orders data for November, which will be released on Tuesday. Orders are estimated to have declined by 0.4% after expanding by 0.3% in October.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling consolidates but death cross shows bearish bias
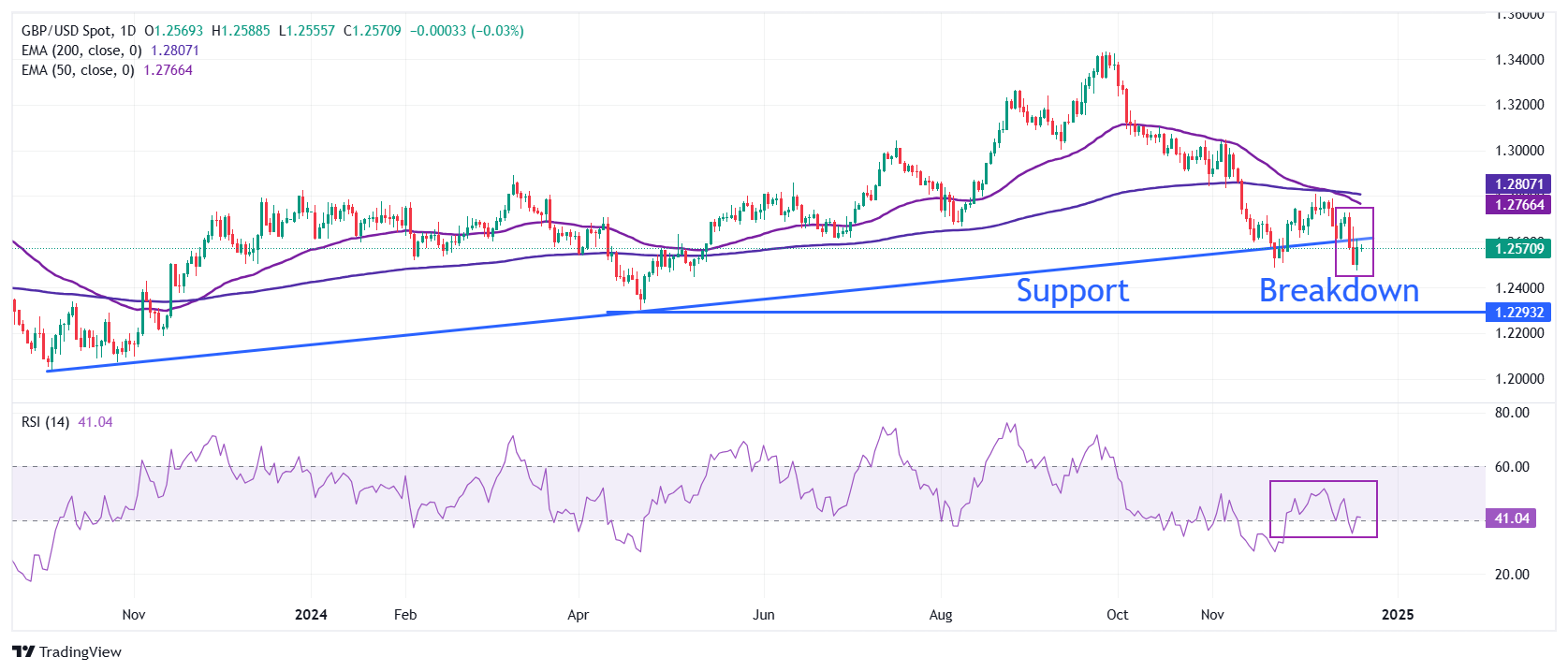
The Pound Sterling broadly consolidates against the US Dollar after a decisive break below the upward-sloping trendline around 1.2600, which is plotted from the October 2023 low of 1.2035.
A death cross, represented by the 50-day and 200-day Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs) near 1.2790, suggests a strong bearish trend in the long run.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) rebounds above 40.00. A fresh downside momentum could trigger if the oscillator fails to sustain above that level.
Looking down, the pair is expected to find a cushion near the April 22 low around 1.2300. On the upside, the December 17 high at 1.2730 will act as key resistance.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.







