EUR/USD eases back after misfire in EU PMI figures

- EUR/USD declined in one of its worst days in H2 2024.
- EU PMI figures broadly came in below expectations, while US PMIs also printed lower.
- Tuesday is set to be a quiet day on the Fiber front.
EUR/USD trimmed recent bullish momentum, declining by one-half of one percent on Monday. Fiber declined in one of its worst trading days in the second half of the year after pan-EU Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) figures broadly missed expectations, while the US PMI data print faired only slightly better.
Tuesday will be a quiet affair on the EUR/USD front; little data is expected from either side of the Atlantic, though Federal Reserve (Fed) Governor Michelle Bowman is expected to make an appearance.
Despite a broad-market weakening in the Greenback following last week’s surprise double rate cut from the Fed, souring market sentiment on behalf of the Euro is keeping EUR/USD under wraps.
September’s S&P US Manufacturing PMI declined to 47.0 MoM, falling to its lowest level since July of 2023 as the US manufacturing sector sees a continued gloomy outlook on business activity. On the other hand, the S&P US Services PMI eased to 55.4 in September, down from August’s 55.7 but beating the expected print of 55.2.
Fed policymaker and Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee hit markets with cooling comments early Monday, noting that much further movement on rates from the Fed could be necessary. The Fed official highlighted that the Fed may need to shoot much lower on policy rates in order to keep business lending conditions sufficiently liquid enough to keep the US business landscape keel-side down as record tightness in the US labor market drains away.
EUR/USD price forecast
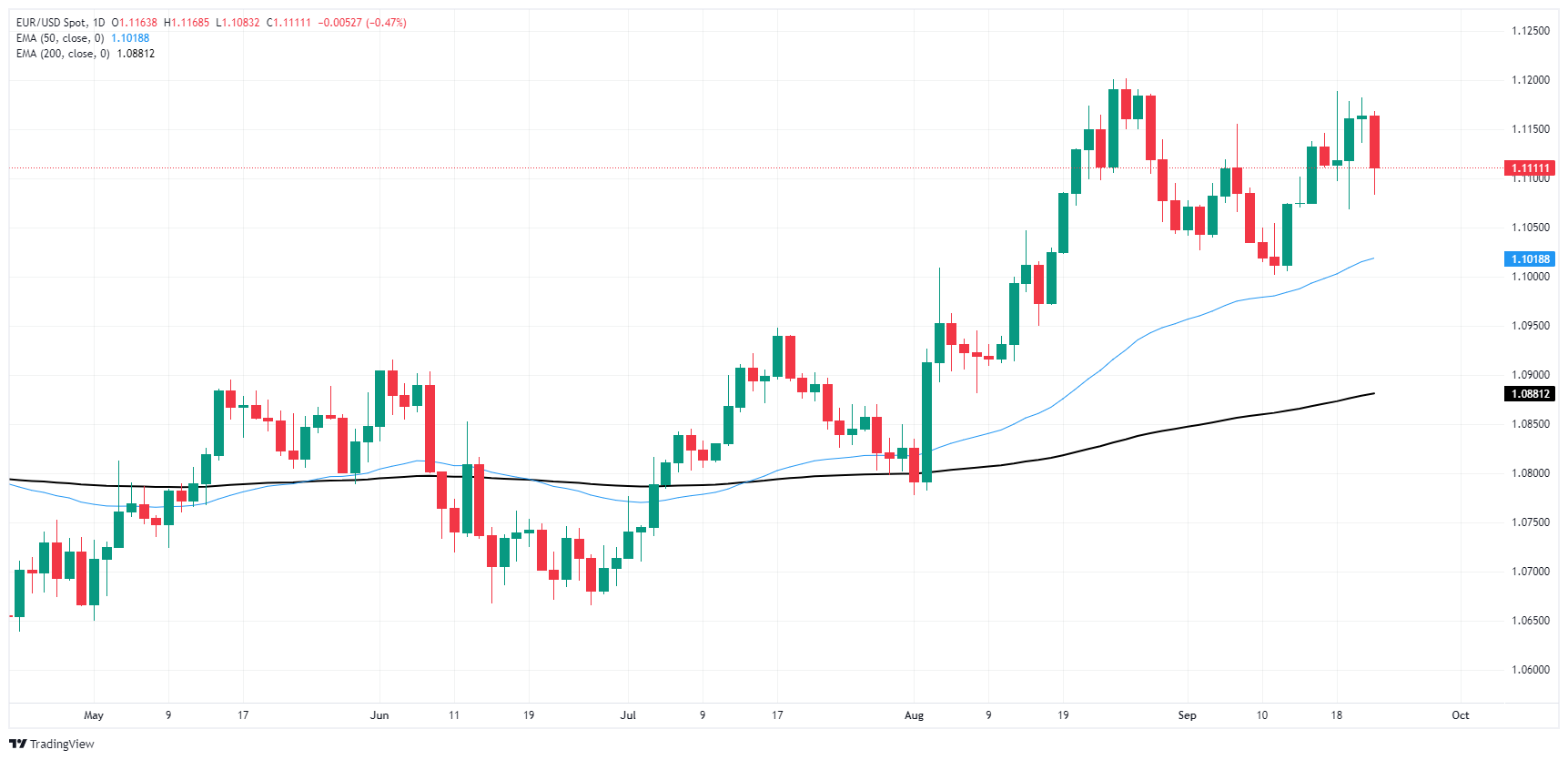
Fiber continues to get mired into the 1.1100 handle, and bulls are beginning to show signs of exhaustion from battling price action into the top end of near-term momentum. Despite intraday weakness, EUR/USD continues to remain overall well-bid, with the pair testing into yearly highs despite an inability to reclaim the 1.1200 handle.
EUR/USD daily chart
Euro FAQs
What is the Euro?
The Euro is the currency for the 20 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
What is the ECB and how does it impact the Euro?
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
How does inflation data impact the value of the Euro?
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
How does economic data influence the value of the Euro?
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
How does the Trade Balance impact the Euro?
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.