EUR/USD consolidates as investors look for fresh guidance on Fed-ECB rate-cut path

- EUR/USD trades sideways above 1.0900 amid uncertainty over Fed-ECB interest rates.
- The ECB is expected to deliver two more rate cuts this year.
- Lower-than-expected US Initial Jobless Claims offered relief to widespread risk-aversion.
EUR/USD trades sideways above the round-level support of 1.0900 in Friday’s European session. The major currency pair trades inside Thursday’s trading range, with investors looking for fresh cues indicating how much the European Central Bank (ECB) and the US Federal Reserve (Fed) will cut interest rates this year.
The ECB is expected to cut interest rates two times more this year as the Eurozone economy is going through a rough phase, and price pressures are on track to return to the desired rate of 2%. However, ECB officials continue to refrain from committing to a pre-defined rate-cut path as they expect the way towards the central bank’s target of 2%.
On Wednesday, Finnish ECB policymaker Olli Rehn said in a speech, "Inflation continues to slow down but the path to the two percent target remains bumpy this year." “He added the rate cuts would help the eurozone economy recover, in particular the "fragile" industrial growth and subdued investments,” Reuters reported.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD steadies as US Dollar edges lower
- EUR/USD holds gains above 1.0900 as the US Dollar (USD) drops on firm Fed rate-cut prospects. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, trades near 103.00 after correcting from a four-day high of 103.50.
- The expectations for Fed rate cuts rose significantly this week after the weak United States (US) Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report for July published last Friday, which prompted fears that the economy is entering a recession. This bolstered risk aversion, which caused global equity markets to face an intense sell-off on Monday.
- Meanwhile, fears of a weakening US labor market have been diminished by lower-than-expected Initial Jobless Claims for the week ending August 2. The data showed on Thursday that the number of individuals claiming jobless benefits for the first time came in lower at 233K than estimates of 240K and the prior release of 250K (upwardly revised from 249K).
- Commenting on the latest jobless claims print, Gennadiy Goldberg, head of US rates strategy at TD Securities in New York, said: “This is a very positive print for markets overall. It reinforces the fact that labor market momentum is not slowing to the same extent that was represented by the payroll report, and it also reinforces the absence of very significant layoffs in the economy.”
- According to the CME FedWatch tool, investors are divided over the size of Fed rate cuts in September. 30-day Federal Funds futures pricing data shows that traders see a 54.5% chance that interest rates will be reduced by 50 bps in September, down from 74% recorded a week ago.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD holds 200-day EMA
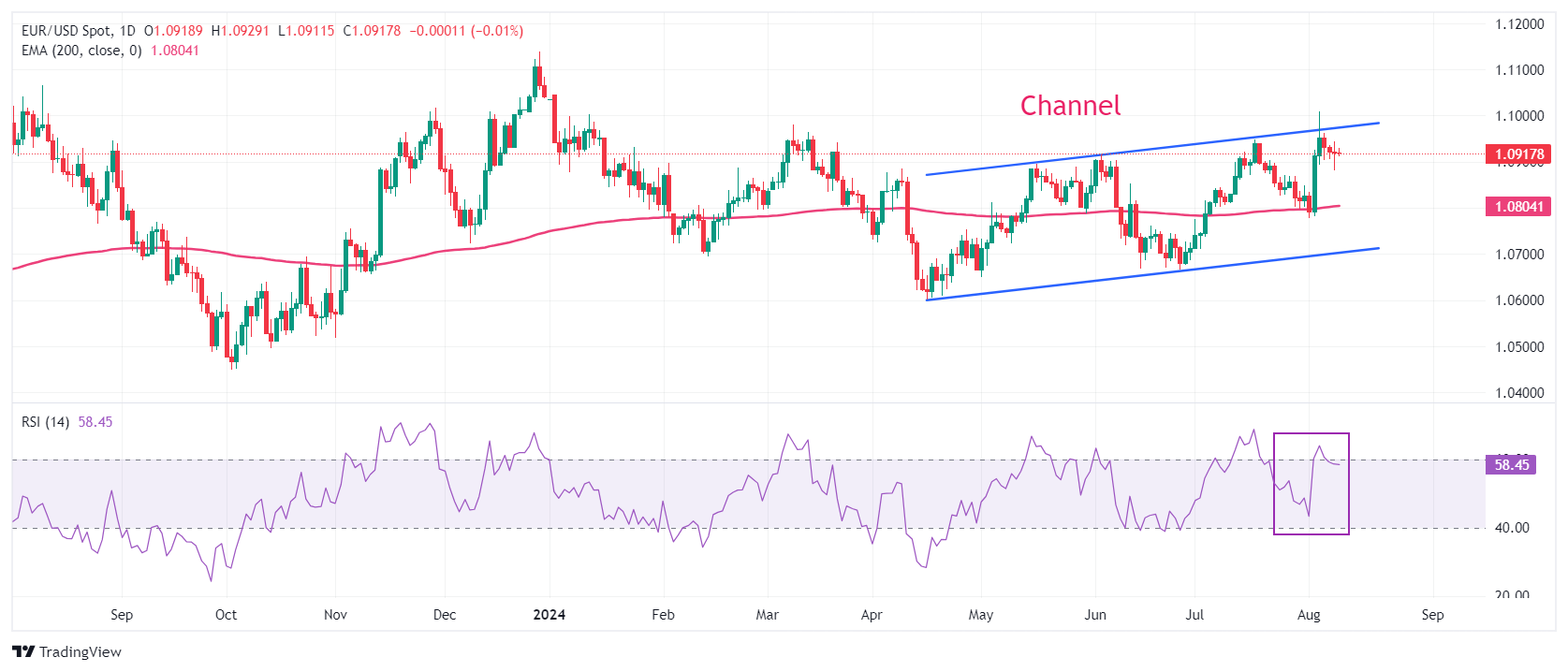
EUR/USD trades near the upper boundary of a Channel formation on a daily timeframe. A breakout of the aforementioned chart pattern results in wider ticks on the upside and heavy volume. The 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), near 1.0800, acted as major support for the Euro bulls.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicator returns inside the 40.00-60.00 range. If the RSI rises above 60.00, bullish momentum will be triggered.
More upside would appear if the major currency pair breaks above Monday’s high of 1.1009. This would drive EUR/USD towards the August 10, 2023, high at 1.1065, followed by the round-level resistance at 1.1100.
In an alternate scenario, a downside move below the August 1 low at 1.0777 would drag the pair toward the February low near 1.0700. A breakdown below the latter would expose the asset to the June 14 low at 1.0667.
Euro FAQs
What is the Euro?
The Euro is the currency for the 20 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
What is the ECB and how does it impact the Euro?
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
How does inflation data impact the value of the Euro?
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
How does economic data influence the value of the Euro?
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
How does the Trade Balance impact the Euro?
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.







