EUR/USD gains firm footing above 1.0700 amid cheerful market mood

- EUR/USD rises to 1.0740 even though Germany’s outlook appears to be dull.
- The ECB could deliver subsequent rate cuts to uplift poor demand prospects.
- The US Dollar will dance to the tunes of the US core PCE inflation data for May.
EUR/USD extends its recovery to 1.0740 in Tuesday’s European session. The major currency pair raises as growing optimism for the Federal Reserve (Fed) to reduce interest rates twice this year has increased investors’ risk appetite.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, has dropped to 105.40 as demand for safe-haven assets has eased. The DXY Index corrects even though the preliminary United States (US) S&P Global Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) unexpectedly beats the consensus and its prior numbers in June.
This week, investors will focus on the US core Personal Consumption Expenditure price index (PCE) for May, which will be published on Friday. The core PCE price index data is the Fed’s preferred inflation measure, and it will provide fresh cues on when and how much the central bank will reduce interest rates this year.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD gains despite Eurozone’s election uncertainty
- EUR/USD rises further to 1.0740 as the market sentiment is favorable for risk-perceived assets. However, the outlook for the Euro is uncertain as economic prospects of Eurozone’s largest economy appear to be deteriorating. German IFO Institute data, which exhibits market sentiment over the economy’s current position and forward outlook, indicated a gloomy picture.
- IFO Business Climate, an early indicator of current conditions and business expectations in Germany, surprisingly declined to 88.6 in June. Investors forecasted a rise to 89.7 from May’s reading of 89.3. In the same period, the Expectations index unexpectedly dropped to 89.0 from the estimates of 91.0 and the former release of 90.3 (downwardly revised from 90.4). On the data release, IFO President Clemens Fuest said, "The German economy is having difficulty overcoming stagnation."
- Last week, the preliminary HCOB PMI data for June also pointed to slowing economic activities due to a sharper decline in new orders from domestic as well as global markets. The Manufacturing PMI contracted at a faster pace and declined to a six-month low of 45.6 from the prior reading of 47.3. The Services PMI continues to expand but at the slowest pace in three months.
- The dismal economic outlook for the Eurozone economy points to subsequent rate cuts from the European Central Bank (ECB). The ECB began unwinding its restrictive interest rate framework in its policy meeting in early June. However, officials have been refraining from committing to any specific rate-cut path as they remain concerned over upside risks to wage inflation, which could boost price pressures.
- Meanwhile, political uncertainty is deepening as France heads toward the first round of snap legislative elections, scheduled for June 30. French President Emmanuel Macron called for a snap election after his party suffered defeat in preliminary results in European parliamentary elections held on June 9 from Marine Le Pen’s far-right National Rally (RN).
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD trades below 50-day EMA
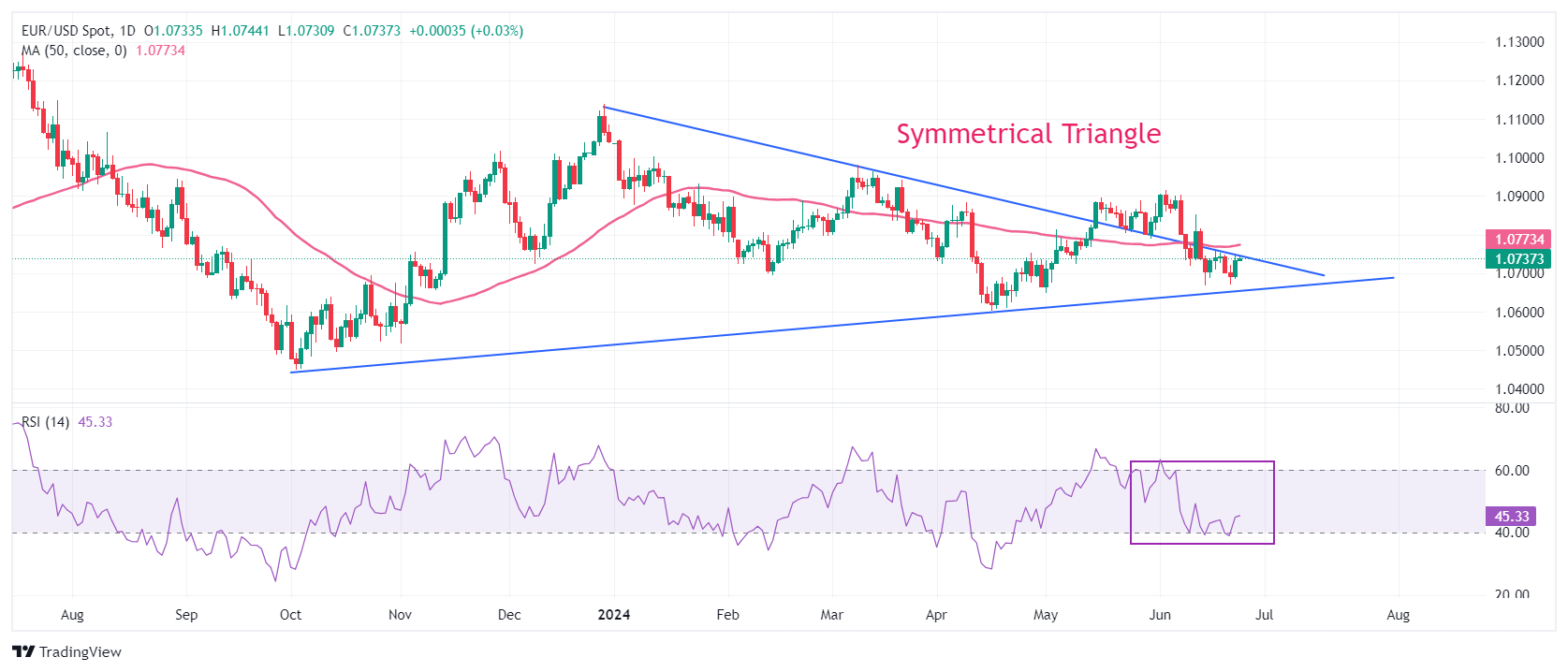
EUR/USD trades close to Monday’s high around 1.0740. The major currency pair continues to face selling pressure near the downward-sloping border of the Symmetrical Triangle near 1.0750, which is plotted from 28 December 2023 high around 1.1140. The pair trades below the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which indicates that the short-term outlook is bearish.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) hovers near 40.00. A bearish momentum would trigger if the oscillator slips below this level.
Euro FAQs
What is the Euro?
The Euro is the currency for the 20 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
What is the ECB and how does it impact the Euro?
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
How does inflation data impact the value of the Euro?
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
How does economic data influence the value of the Euro?
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
How does the Trade Balance impact the Euro?
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.








